Tel:
0755-23027370
Respiratory Topic | Structure and Working Principle of Medical Ventilator
Introduction:
The Medical Ventilator is a medical device that can replace spontaneous ventilation function for the treatment of respiratory diseases such as respiratory failure, pneumonia, asthma, and anesthetic respiratory management during surgery. The Medical Ventilator works like an electronic inflating pump, which delivers gas to our lungs regularly and quantitatively, allowing the body to obtain precious oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide, a metabolic waste. So what is the basic structure of a Medical Ventilator? Let's take a look at the basic components of a Medical Ventilator together.
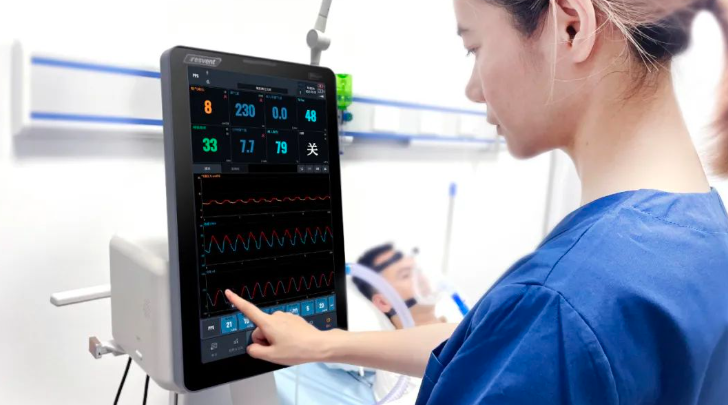
Structure of Medical Ventilator includes
Control Board, Pressure sensor, Flow Sensor, Airway, Turbine,Oxygen import, exhalation valve,humidifier etc.
Control Panel: The core part of the Medical Ventilator, including a touch screen display, a rotation encoder mute button, and a lock screen; used for setting and monitoring various parameters of the Medical Ventilator, such as respiratory frequency, tidal volume, oxygen concentration, etc.
Pressure Sensor: An important component of the Medical Ventilator that can sense the respiratory pressure of the patient and transmit this information to the control panel, allowing healthcare professionals to adjust it according to the needs of the patient.
Flow Sensor: A flow monitoring device used to detect the respiratory flow of the patient for real-time adjustment according to the patient's needs.
Airway: An essential component of the Medical Ventilator that includes various pipes and valves used to deliver oxygen and air to the patient's lungs and expel carbon dioxide out of the body.
Turbo: Turbocharger is actually an air compressor that increases the amount of air by compressing it.
Oxygen Source Port: An interface for delivering oxygen.
Inspiratory Valve: During inspiration, the inspiratory valve opens and the machine supplies air to the patient from one direction.
Expiratory Valve: During expiration, the expiratory valve opens and the expired air is discharged through the expiratory airway.
Humidifier: A constant temperature device that allows water and air to circulate in and out. It protects the patient's lungs from stimulation by cold air, prevents dehydration of the respiratory mucosa, and performs the humidification, filtering, and heating functions similar to those of the human respiratory tract.

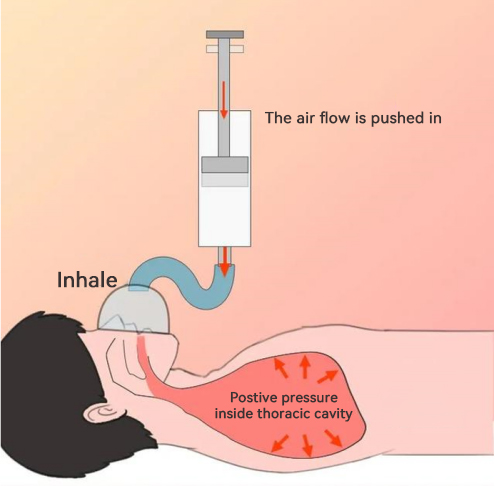
The Medical Ventilator is generally divided into invasive Medical Ventilators and non-invasive Medical Ventilators, which are often used with high-flow oxygen therapy. What is the difference between them?
【1】High-flow oxygen therapy refers to the continuous provision of a regulated and relatively constant oxygen concentration for patients, which can be used to treat patients with respiratory failure and improve their PaO2, SaO2, etc., but cannot improve the patient's Medical Ventilatory capacity.
【2】Non-invasive Medical Ventilator is a non-invasive respiratory support device that does not require intubation into the trachea. Instead, it delivers oxygen to the patient through a mask or nasal prongs to improve respiratory function and gas exchange capacity. It can be used for the treatment of various respiratory diseases; such as sleep apnea syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cardiac pulmonary edema.
【3】The basic principle of invasive and non-invasive Medical Ventilators is the same, but the biggest difference is that invasive Medical Ventilators require intubation of the patient into the trachea. This ensures that the gas delivered by the Medical Ventilator can reach the lungs through the tracheal tube.
【4】For patients without spontaneous breathing, high-flow oxygen therapy and non-invasive Medical Ventilators may not be able to deliver treatment gases to a significant portion of the respiratory tract due to leakage.

"Resvent Medical Ventilator has functions of invasive, non-invasive, and oxygen therapy. Clinical healthcare professionals can choose the appropriate function according to the patient's condition."
Medical Ventilators are crucial for patients with respiratory failure, mainly relying on Medical Ventilators to maintain their life. The emergence of Medical Ventilators provides respiratory support for patients with respiratory failure, allowing doctors to rescue patients and treat diseases in a timely manner and creating conditions for treatment.